Brain Disease Model Of Addiction: Why Is It So Controversial?
Brain disease model of addiction: why is it so controversial?. This commentary Volkow Koob 2016 cites the scientific evidence for and advantage of the brain disease model of addiction. However these claims are not supported by the evidence. The Personal View by Wayne Hall and colleagues1 questions the value of the brain disease model of addiction BDMA and claims that it is not supported by animal or neuroimaging evidence that it has not helped deliver more effective treatments and that its impact on public policy has been modest.
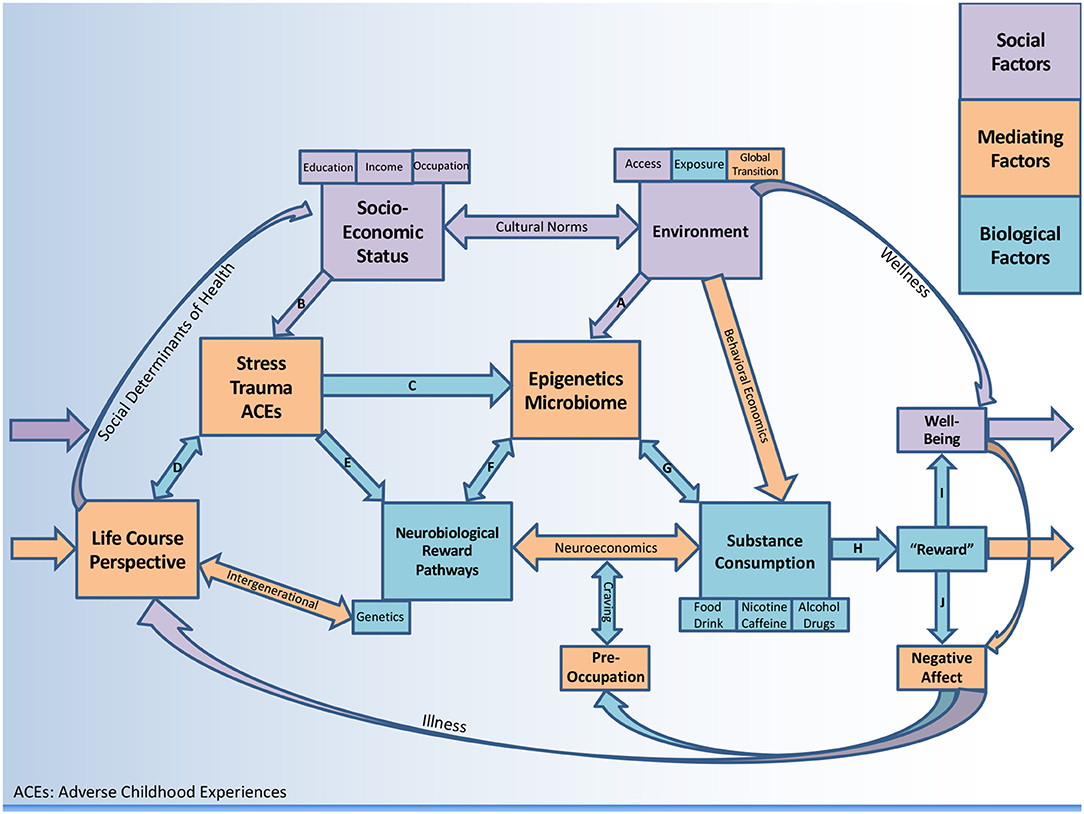
Why is it so controversial. Additional criticisms of the concept of addiction as a brain disease include the failure of this model to identify genetic aberrations or brain abnormalities that consistently apply to persons. Brain disease model of addiction.
Brain disease model of addiction. Proponents of the brain-disease model of addiction have argued that a neuroscience perspective on addiction reduces the attribution of free will because it relocates the cause of the disorder to the brain rather than to the person thereby diminishing the blame attributed to the person with an addiction. However these claims are not supported by the evidence.
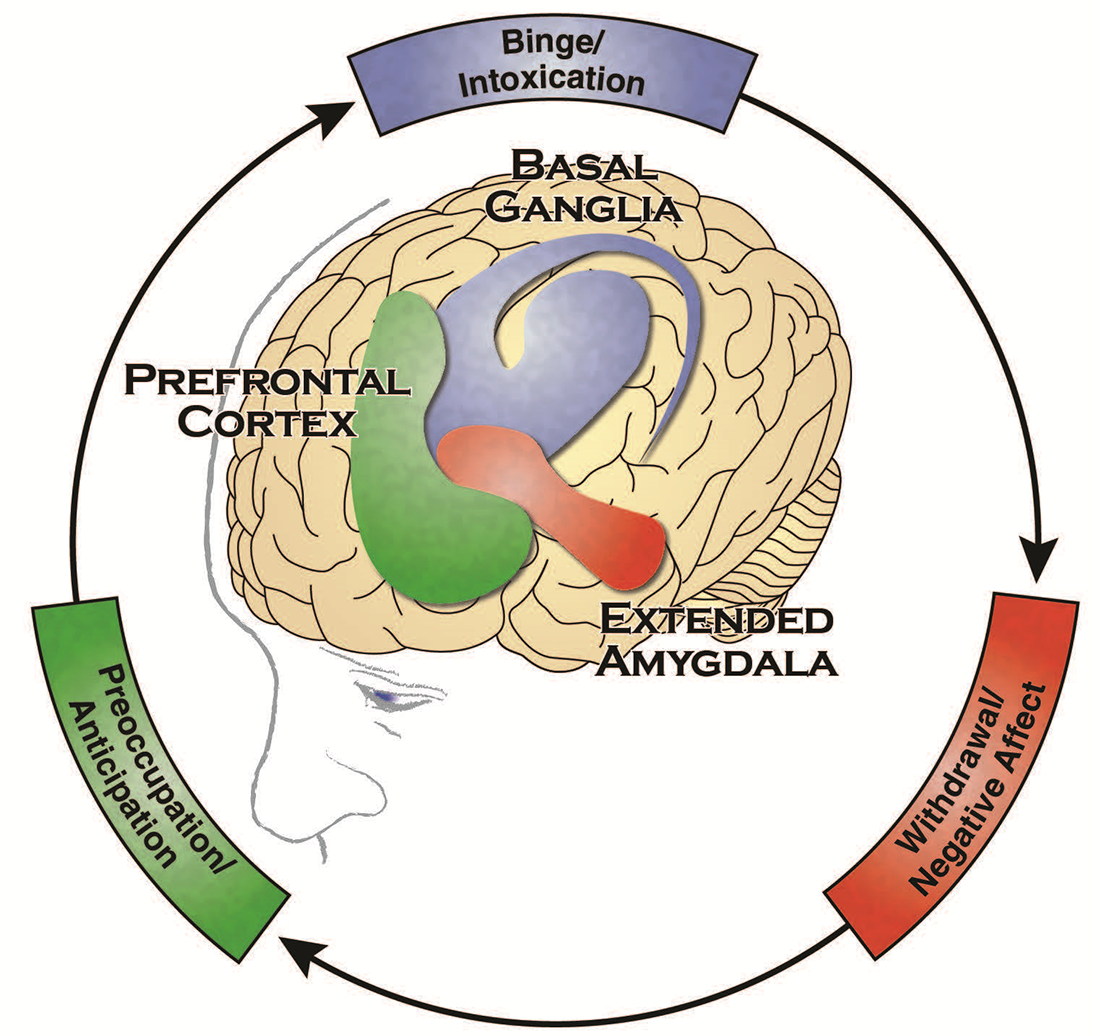
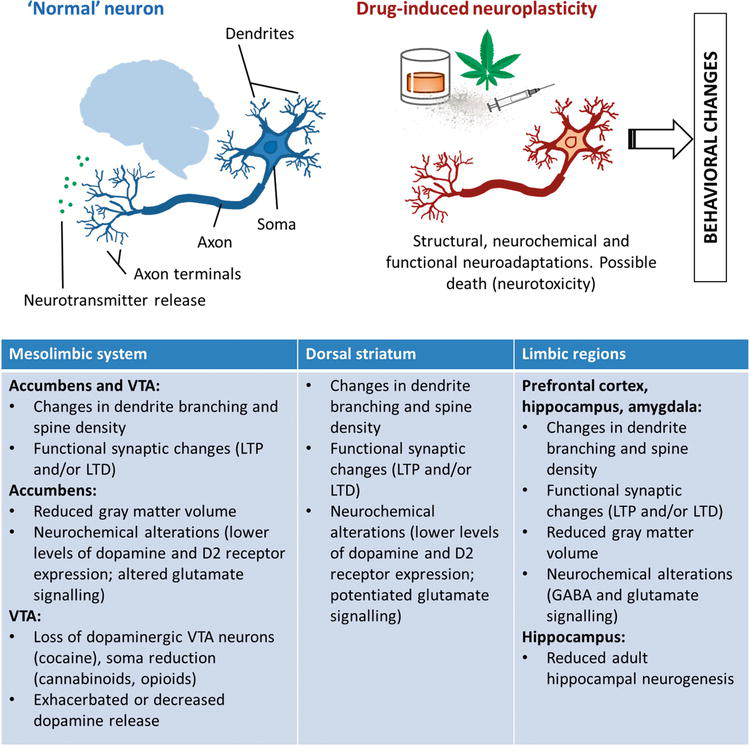
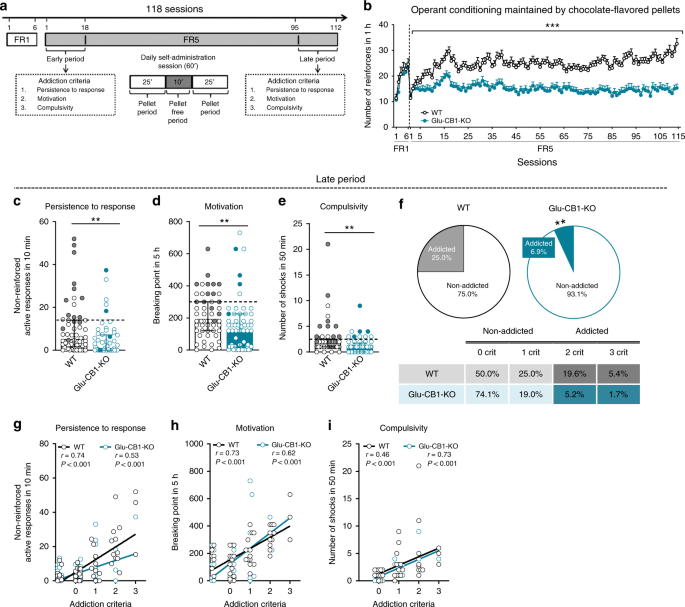
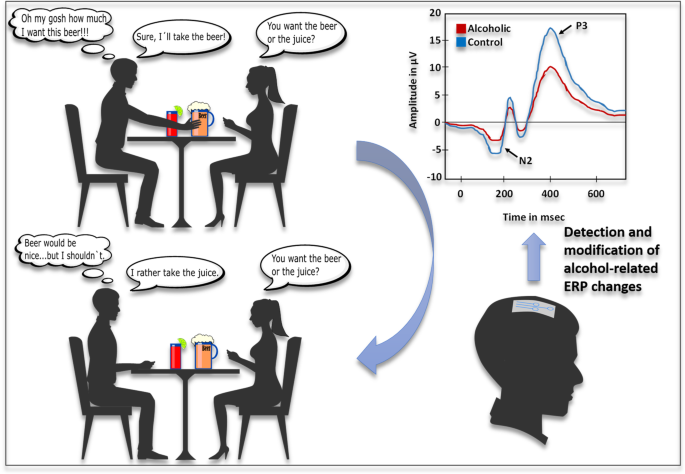
In the simplest of terms the disease model of addiction states that addiction is a relapsing brain disorder characterized by the altered structure and functioning of the brain. These changes occur over time. Volkow MD Director National Institute on Drug Abuse and George Koob PhD Director National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism published online July 29 2015 in.
First preclinical and clinical. Brain disease model of addiction. The Personal View by Wayne Hall and colleagues1 questions the value of the brain disease model of addiction BDMA and claims that it is not supported by animal or neuroimaging evidence that it has not helped deliver more eff ective treatments and that its impact on.
We were disappointed by Nora Volkow and George Koobs response 1 to our critique 2 of the brain disease model of addiction BDMA from the US National Institute on Drug Abuse NIDA which simply repeats the promise of future treatment advances and puts the most favourable spin on modest treatments that have been used since Alan Leshner first promulgated the BMDA in 1997. In 1998 Leshner testified that NIDA supports more than 85. The Personal View by Hall Carter and Forlini 1 questions the value of the BDMA brain disease model of addiction and claims that it is not supported by animal or neuroimaging evidence that it has not helped deliver more effective treatments and that its impact on public policy have been modest.
Volkow ND Koob G. Authors Nora D Volkow 1 George Koob 2 Affiliations.
We were disappointed by Nora Volkow and George Koobs response 1 to our critique 2 of the brain disease model of addiction BDMA from the US National Institute on Drug Abuse NIDA which simply repeats the promise of future treatment advances and puts the most favourable spin on modest treatments that have been used since Alan Leshner first promulgated the BMDA in 1997.
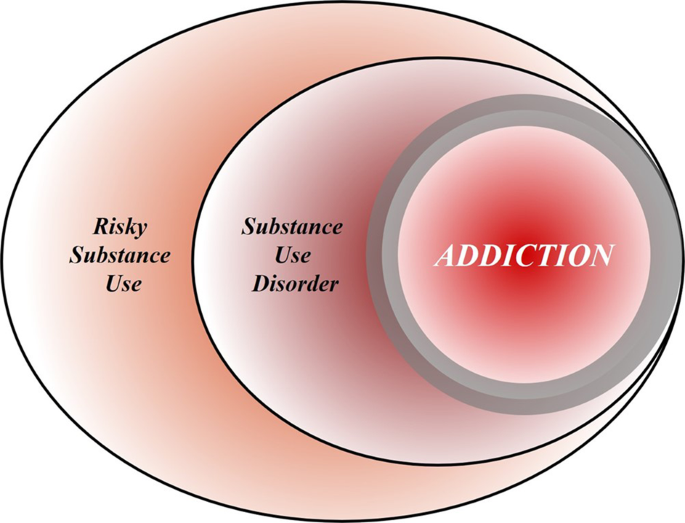
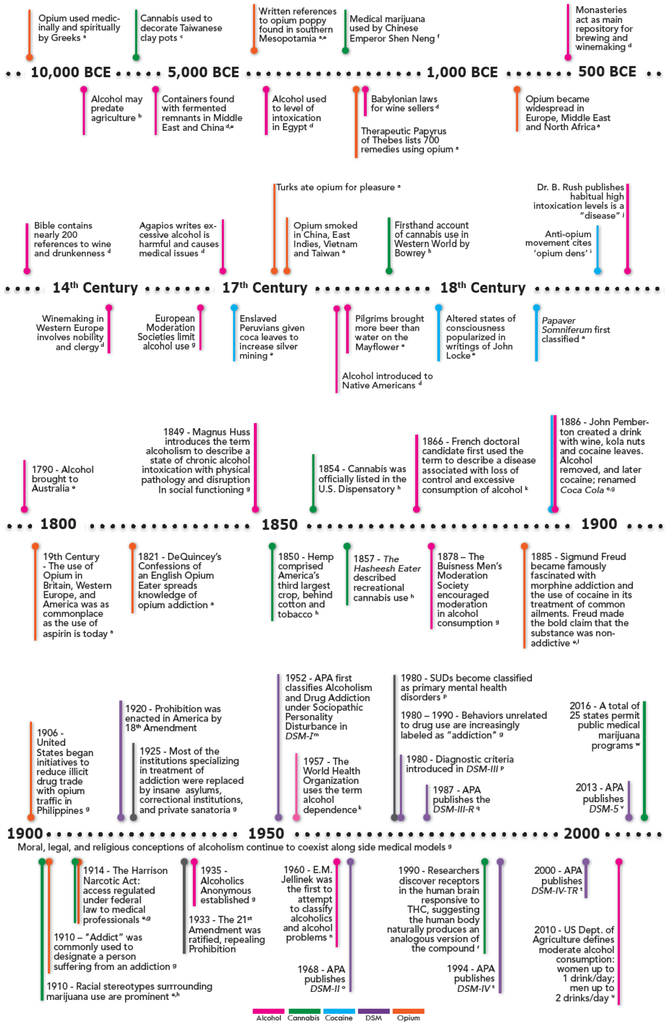
A person must begin abusing alcohol or drugs and then continue abusing alcohol or drugs for a prolonged period of time. The commentary is a direct response to the criticism published by Hall Carter and Forlini 2015. Brain disease model of addiction. Why is it so controversial. Brain disease model of addiction. Why is it so controversial. However these claims are not supported by the evidence. The brain disease model of addiction holds that SUDs are chronic relapsing brain diseases and that relapses are symptoms and part of the. We were disappointed by Nora Volkow and George Koobs response 1 to our critique 2 of the brain disease model of addiction BDMA from the US National Institute on Drug Abuse NIDA which simply repeats the promise of future treatment advances and puts the most favourable spin on modest treatments that have been used since Alan Leshner first promulgated the BMDA in 1997.
These changes occur over time. Proponents of the brain disease model of addiction BDMA have been very influential in setting the funding priorities of NIDA and by extension the bulk of publically supported research on addiction. First preclinical and clinical. This commentary Volkow Koob 2016 cites the scientific evidence for and advantage of the brain disease model of addiction. PMID26249284 PMCIDPMC4556943 Abstract Citations. In the simplest of terms the disease model of addiction states that addiction is a relapsing brain disorder characterized by the altered structure and functioning of the brain. Why is it so controversial.






























Post a Comment for "Brain Disease Model Of Addiction: Why Is It So Controversial?"