Polycystic Kidney Disease In Fetus
Polycystic kidney disease in fetus. 2569078 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types. A molecular prenatal diagnosis was performed at 10 weeks on fetus 2 a sib of fetus 1. What is Polycystic Kidney Disease.
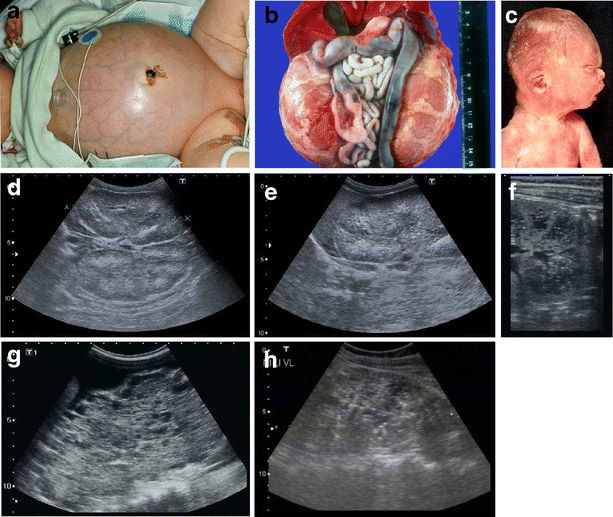
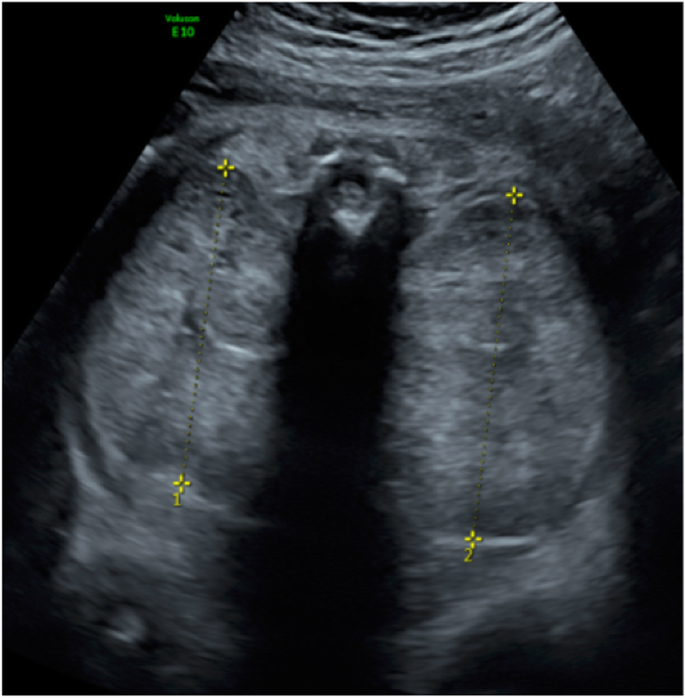
5 10 VACTERL Cerebro digital syndrome tuberous sclerosis Extra-renal. Autosomal recessive renal polycystic kidney disease ARPKD is a rare form of cystic kidney disease occurring in approximately 1 in 20000 live births 1. Ultrasound scans every 4 weeks to assess amniotic fluid volume.
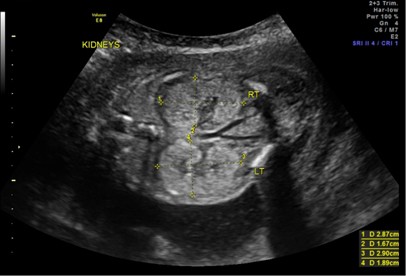
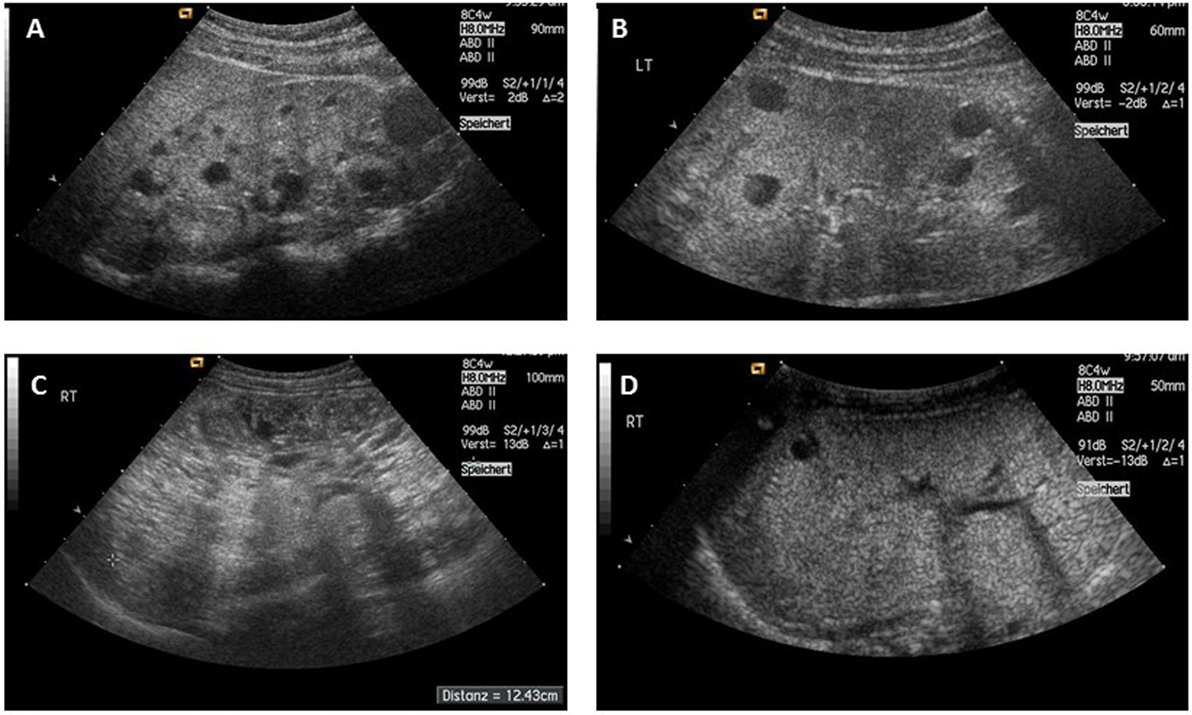
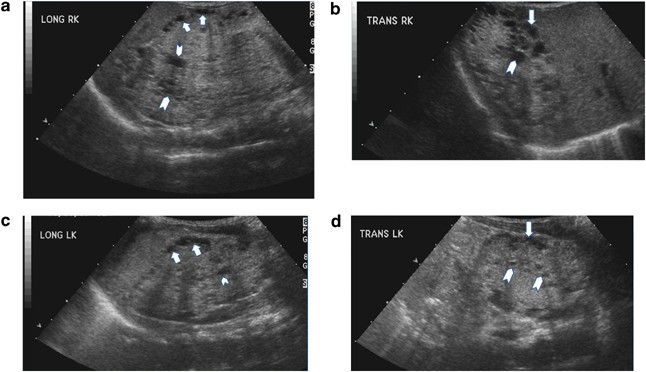
Fetus 1 was diagnosed at 20 weeks of gestation by ultrasonography. We report on 3 cases with a fetal presentation of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD which illustrate the variable expression of ADPKD during fetal life. It accounts for about 90 of all PKD cases.
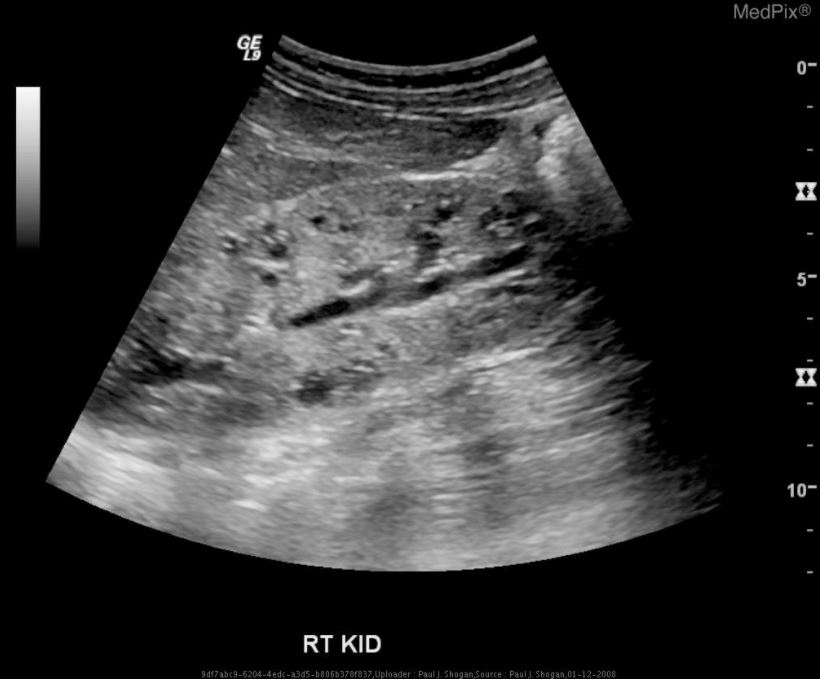
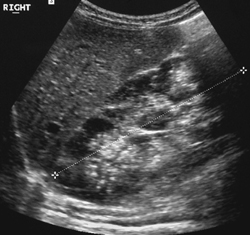
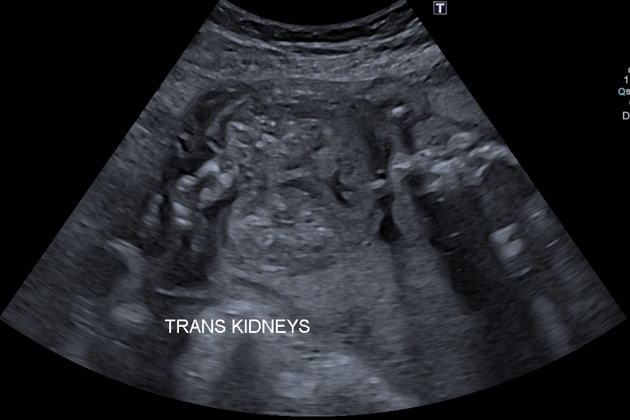
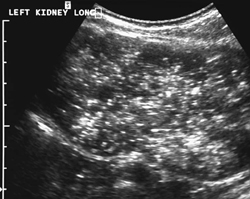
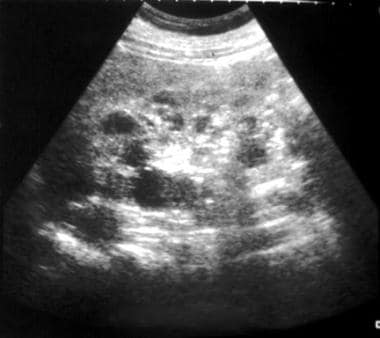
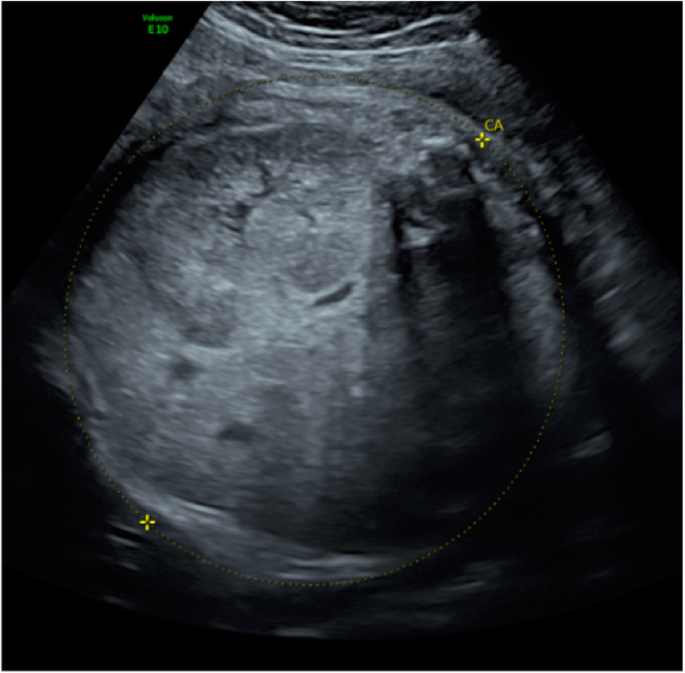
Bilaterally enlarged and homogeneously hyperechogenic kidneys. Usually found 24 weeks gestation. A molecular prenatal diagnosis was performed at 10 weeks on fetus 2 a sib of fetus 1.
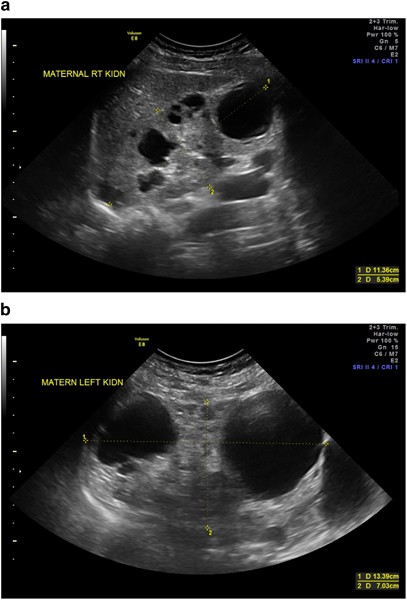
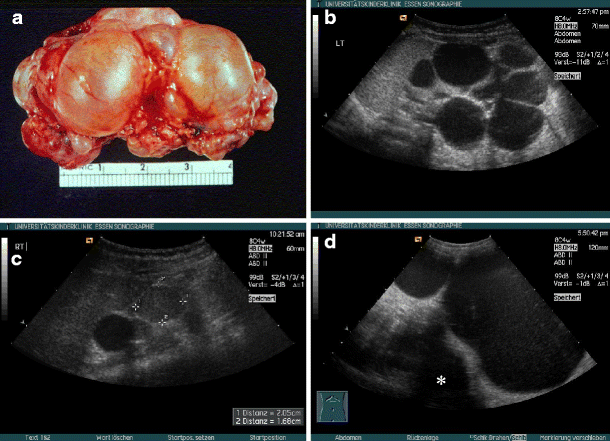
Prenatal ultrasonography results were correlated with positive family history of polycystic kidney disease PKD fetal enlarged kidneys and oligohydramnios. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease ARPKD is a rare genetic disorder that affects 1 in 20000 children. The disease has a wide spectrum of renal and hepatic involvement and it is subdivided into perinatal neonatal infantile and juvenile types on the basis of the age of onset of the clinical presentation.
It is caused by mutations in the PKHD1 polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 gene situated on chromosome 6p12 which encodes for the protein fibrocystin 2. Both males and females are equally affected. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is the most common form of PKD.
Fetus 1 was diagnosed at 20 weeks of gestation by ultrasonography. However doctors refer to the problems that arise in the development of the urinary tract in the fetus as congenital.
Hydronephrosis occurs when a blockage makes the urine return to the kidneys.
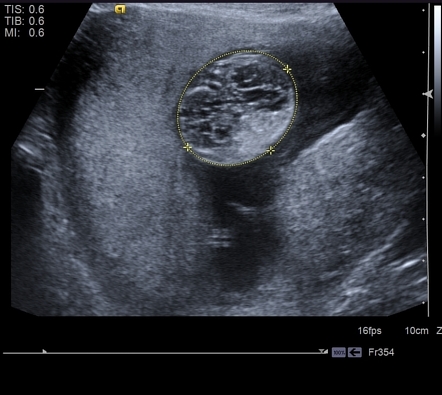
An unusual case of fetal polycystic kidney disease is reported. Prenatal ultrasonography results were correlated with positive family history of polycystic kidney disease PKD fetal enlarged kidneys and oligohydramnios. What is Polycystic Kidney Disease. ADPKD is often diagnosed in adulthood. Autosomal dominant means that if one parent has the disease there is a 50 chance that the disease will pass to a child. We report on 3 cases with a fetal presentation of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD which illustrate the variable expression of ADPKD during fetal life. And ADPKD was an incidental finding in fetus 3 who was aborted at 16. 5 10 VACTERL Cerebro digital syndrome tuberous sclerosis Extra-renal. However doctors refer to the problems that arise in the development of the urinary tract in the fetus as congenital.
Autosomal dominant means that if one parent has the disease there is a 50 chance that the disease will pass to a child. Polycystic Kidney Disease PKD is a genetic disease characterized by the growth of numerous fluid-filled cysts that can result in malformed or enlarged kidneys. Polycystic kidney disease PKD is a genetic disorder that causes the growth of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. Polycystic kidney disease in the fetus. The disease is caused by mutations in the PKD1 gene 85 of cases on chromosome 16p1313 and PKD2 gene 15 of cases on chromosome 4q1323. An unusual case of fetal polycystic kidney disease is reported. And ADPKD was an incidental finding in fetus 3 who was aborted at 16.




























Post a Comment for "Polycystic Kidney Disease In Fetus"